TB and Respiratory
Causes :-
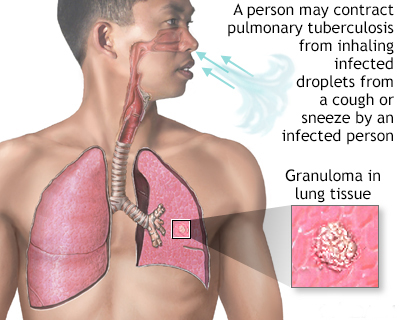
Pulmonary TB is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M tuberculosis). TB is contagious. This means the bacteria are easily spread from an infected person to someone else. You can get TB by breathing in air droplets from a cough or sneeze of an infected person. The resulting lung infection is called primary TB.
Most people recover from primary TB infection without further evidence of the disease. The infection may stay inactive (dormant) for years. In some people, it becomes active again (reactivates).
The following people are at higher risk of active TB or reactivation of TB:
Older adults
Infants
People with weakened immune systems, for example due to HIV/AIDS, chemotherapy, diabetes, or medicines that weaken the immune system.
Your risk for catching TB increases if you:
Have poor nutrition
Are around people who have TB
Live in crowded or unclean living conditions.
The following factors can increase the rate of TB infection in a population:
Increase in HIV infections.
Presence of drug-resistant strains of TB.
Increase in number of homeless people (poor environment and nutrition).
Symptoms :-
The primary stage of TB does not cause symptoms. When symptoms of pulmonary TB occur, they can include:
Breathing difficulty
Chest pain
Cough (usually with mucus)
Coughing up blood
Excessive sweating, particularly at night
Fatigue
Fever
Weight Loss
Wheezing